Scaling Up Video Management Systems(VMS)
Scaling Up Video Management Systems(VMS)

What is a video management system?
Video Management Systems, also known as VMS, collect inputs from multiple cameras and other sensors, addressing all related aspects of video handling, such as storage, retrieval, analysis and display. VMS are typically used in the security and surveillance space, enhancing personal safety in public areas, office buildings, transportation terminals, medical institutes, and more. Other typical uses include the extraction of business intelligence through user behavior analysis for the purpose of customer experience improvement in retail and other industries.
Traditionally, the analysis of multiple video streams used to be laborious, relying on human perception for visual identification of events happening across a multitude of video feeds. This method has many disadvantages as it is difficult to scale, violates people’s privacy, and is prone to errors due to operator’s fatigue, leading to false alarms, missed occurrences, and inefficient use of resources.
Nowadays, deep learning is enabling the automation of video analytics tasks, thereby allowing for scalability, and improvement in overall performance. This eventually leads to lower total cost of ownership (TCO).
According to a recent market research, the video management system market size is expected to reach $31B by 2027, growing at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 23.1% between 2022-2027. The key drivers for this growth are increasing security concerns and rapid adoption of IP cameras for surveillance, security, and retail applications.
AI-powered video analytics are being rapidly adopted for VMS
There are multiple possible configurations to a VMS system, depending on the number of video channels, the required video analytics applications, and the system cost. However, a typical video management system will include, in addition to cameras, an NVR or VMS server, a display (mobile phone, single or multiple screens, etc.) and storage space (local or cloud-based).
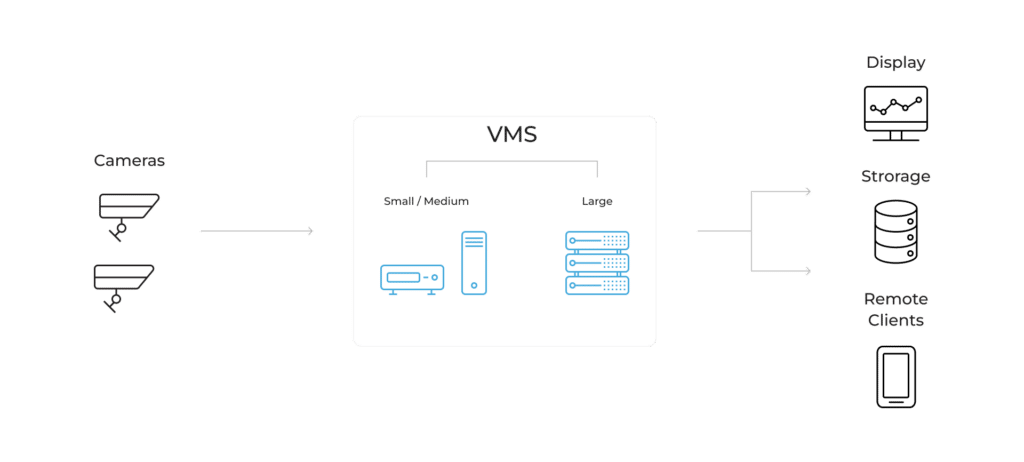
To enable real-time and accurate video analytics, Video Management Systems require high-performance computing. Artificial intelligence (AI) is transformational to this market as it allows faster and more accurate event identification at a lower cost. For this reason, AI-powered video analytics are being rapidly adopted by VMS software providers. AI video analytics could be introduced to any and all of the system components, e.g., at the data source on smart cameras, at the aggregation point such as smart gateways or network video recorders (NVRs), or in the cloud, which is sometimes administered as a service (VSaaS – video surveillance as a service). For a more detailed review of the different VMS configurations and how to design AI into each of them, refer to our whitepaper.
Introducing AI to the different system components provides multiple benefits:
- Enhanced safety – spotting relevant events, hazards, and regions of interest (ROIs) in each video stream, triggering response to pre-defined events, creating video metadata to enable history search, and enabling anonymization for improved privacy
- Improved network utilization – streaming relevant events only reduces bandwidth which results in further cost saving
- Improved storage utilization – removing irrelevant or uninteresting content to minimize storage space and enhance cost-efficiency
AI is fundamental for more accurate and safer VMS
The use of AI-powered video analytics in VMS is threefold: event detection, response triggering and data analysis.
Detect
The first layer of video analytics is scene understanding and metadata extraction for the purpose of both real-time response as well as long term storage for future search and analysis. Multiple neural networks can be deployed for this phase, leveraging advanced algorithms to perform deep-learning tasks. These tasks serve as the foundation on which more complex tasks identify pre-defined events and trigger specific response.
- Object Recognition – identify specific objects or a class of objects within a frame, and could be used to distinguish between classes of objects
- Counting – count the number of objects in a specific area, especially in places where occupancy is limited and has safety implications
- Density estimation – identify an evolving situation. Unlike counting, this is relevant in cases in which the exact number of objects is not required, but rather their overall density
- Object attributes – assist in unique identification of a person or an object in a specific scene, or re-identification of the same unique entity in the same scene over time, or across multiple scenes
- Gesture estimation – analyze a sequence of gestures which enables interpretation of specific behaviors for the purpose of behavioral analysis
- Distance measurement – calculate the distance between two or more people or objects, based on the accurate 3D location of each entity in a defined space
Respond
The second layer of video analytics is real-time event triggering based on insights from the detection phase. In this phase, pre-defined events trigger specific responses, such as setting off an alarm or alerting operators, security personnel or first responders, or triggering end-point actuators, for example to grant access for authorized personnel.
A few common applications used for AI-based response are:
- Crowd Management – through people and vehicle counting, and density estimation, the accumulation of large number of entities creates an event in a specific location which may trigger a response or call to action such as load balancing and dynamic traffic management
- Perimeter Protection – face and person attributes as well as gesture estimation and distance measurement, can all serve to secure and protect an area with restricted access or an unsafe zone
- Social Distancing – detecting whether people maintain social distancing in public places, supporting health authorities in their effort to contain a pandemic
- Behavioral Analysis – recognizing distress signals and triggering an alert to call first responders to the scene as soon as possible, and much faster than a call to 911 would
- Lost Person / Unattended Object – helpful for security personnel searching for lost people/luggage, or tracking down suspects, based on property indexing and gesture estimation
- License Plate Recognition (LPR) – used for access control and billing in parking lots or garages
Analyze
The third layer in video analytics is indexing, storage and retrieval of metadata.
Artificial intelligence is leveraged to cost-efficiently index and store relevant information from video streams. Deep, actionable insights can be extracted by exploring patterns over long-term observations and joint analysis of multiple points of view. This can be employed for the following purposes:
- Indexing & Recording – efficiently manage the data and reduce communication and storage costs, artificial intelligence is used to differentiate between meaningful events and background footage. This enables the system to record and store only significant events as defined by the user
- Summarization – used to create an edited and concise digest of the camera input, which only includes the significant events and insights, cropping out irrelevant footage
-
Data Extraction – Identifying patterns in stored data, based on the metadata extracted from the video stream. The better, and more elaborate this metadata is, the better the results and insights will be. The quality of the metadata relies on the quality of the analytics, and this is where advanced algorithms exhibited by deep learning
,come into play
https://hailo.ai/zh-hans/blog/ai-enhanced-video-management-scalability/
Solutions
AI Inference
Banking
Restaurant / POS
Medical
Security
Factory Automation
CANbus Application
Transportation
Kiosk and Self-service
Public Utilities
AI Inference
-
AICH1000 - AI Accelerator Kit powered by Hailo-8R
-
AI Surveillance Optimization - high efficiency, low consumption & flexible deployment
-
Scaling Up Video Management Systems(VMS)
-
Generative AI for Smart Cockpit / IVI
-
AI In Smart Retail
-
Hailo AI Processor for Personal Computers
-
Access Control & Identity Management
-
Intelligent Transportation Systems
-
Perimeter Protection
-
Hailo AI Processor for AOI
-
Hailo AI Processor for ADAS & AD
-
Optimize medical machines to improve accuracy and efficiency
-
PCB Manufacturing Intelligent AOI System
Scaling Up Video Management Systems(VMS)
Scaling Up Video Management Systems(VMS)

What is a video management system?
Video Management Systems, also known as VMS, collect inputs from multiple cameras and other sensors, addressing all related aspects of video handling, such as storage, retrieval, analysis and display. VMS are typically used in the security and surveillance space, enhancing personal safety in public areas, office buildings, transportation terminals, medical institutes, and more. Other typical uses include the extraction of business intelligence through user behavior analysis for the purpose of customer experience improvement in retail and other industries.
Traditionally, the analysis of multiple video streams used to be laborious, relying on human perception for visual identification of events happening across a multitude of video feeds. This method has many disadvantages as it is difficult to scale, violates people’s privacy, and is prone to errors due to operator’s fatigue, leading to false alarms, missed occurrences, and inefficient use of resources.
Nowadays, deep learning is enabling the automation of video analytics tasks, thereby allowing for scalability, and improvement in overall performance. This eventually leads to lower total cost of ownership (TCO).
According to a recent market research, the video management system market size is expected to reach $31B by 2027, growing at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 23.1% between 2022-2027. The key drivers for this growth are increasing security concerns and rapid adoption of IP cameras for surveillance, security, and retail applications.
AI-powered video analytics are being rapidly adopted for VMS
There are multiple possible configurations to a VMS system, depending on the number of video channels, the required video analytics applications, and the system cost. However, a typical video management system will include, in addition to cameras, an NVR or VMS server, a display (mobile phone, single or multiple screens, etc.) and storage space (local or cloud-based).

To enable real-time and accurate video analytics, Video Management Systems require high-performance computing. Artificial intelligence (AI) is transformational to this market as it allows faster and more accurate event identification at a lower cost. For this reason, AI-powered video analytics are being rapidly adopted by VMS software providers. AI video analytics could be introduced to any and all of the system components, e.g., at the data source on smart cameras, at the aggregation point such as smart gateways or network video recorders (NVRs), or in the cloud, which is sometimes administered as a service (VSaaS – video surveillance as a service). For a more detailed review of the different VMS configurations and how to design AI into each of them, refer to our whitepaper.
Introducing AI to the different system components provides multiple benefits:
- Enhanced safety – spotting relevant events, hazards, and regions of interest (ROIs) in each video stream, triggering response to pre-defined events, creating video metadata to enable history search, and enabling anonymization for improved privacy
- Improved network utilization – streaming relevant events only reduces bandwidth which results in further cost saving
- Improved storage utilization – removing irrelevant or uninteresting content to minimize storage space and enhance cost-efficiency
AI is fundamental for more accurate and safer VMS
The use of AI-powered video analytics in VMS is threefold: event detection, response triggering and data analysis.
Detect
The first layer of video analytics is scene understanding and metadata extraction for the purpose of both real-time response as well as long term storage for future search and analysis. Multiple neural networks can be deployed for this phase, leveraging advanced algorithms to perform deep-learning tasks. These tasks serve as the foundation on which more complex tasks identify pre-defined events and trigger specific response.
- Object Recognition – identify specific objects or a class of objects within a frame, and could be used to distinguish between classes of objects
- Counting – count the number of objects in a specific area, especially in places where occupancy is limited and has safety implications
- Density estimation – identify an evolving situation. Unlike counting, this is relevant in cases in which the exact number of objects is not required, but rather their overall density
- Object attributes – assist in unique identification of a person or an object in a specific scene, or re-identification of the same unique entity in the same scene over time, or across multiple scenes
- Gesture estimation – analyze a sequence of gestures which enables interpretation of specific behaviors for the purpose of behavioral analysis
- Distance measurement – calculate the distance between two or more people or objects, based on the accurate 3D location of each entity in a defined space
Respond
The second layer of video analytics is real-time event triggering based on insights from the detection phase. In this phase, pre-defined events trigger specific responses, such as setting off an alarm or alerting operators, security personnel or first responders, or triggering end-point actuators, for example to grant access for authorized personnel.
A few common applications used for AI-based response are:
- Crowd Management – through people and vehicle counting, and density estimation, the accumulation of large number of entities creates an event in a specific location which may trigger a response or call to action such as load balancing and dynamic traffic management
- Perimeter Protection – face and person attributes as well as gesture estimation and distance measurement, can all serve to secure and protect an area with restricted access or an unsafe zone
- Social Distancing – detecting whether people maintain social distancing in public places, supporting health authorities in their effort to contain a pandemic
- Behavioral Analysis – recognizing distress signals and triggering an alert to call first responders to the scene as soon as possible, and much faster than a call to 911 would
- Lost Person / Unattended Object – helpful for security personnel searching for lost people/luggage, or tracking down suspects, based on property indexing and gesture estimation
- License Plate Recognition (LPR) – used for access control and billing in parking lots or garages
Analyze
The third layer in video analytics is indexing, storage and retrieval of metadata.
Artificial intelligence is leveraged to cost-efficiently index and store relevant information from video streams. Deep, actionable insights can be extracted by exploring patterns over long-term observations and joint analysis of multiple points of view. This can be employed for the following purposes:
- Indexing & Recording – efficiently manage the data and reduce communication and storage costs, artificial intelligence is used to differentiate between meaningful events and background footage. This enables the system to record and store only significant events as defined by the user
- Summarization – used to create an edited and concise digest of the camera input, which only includes the significant events and insights, cropping out irrelevant footage
-
Data Extraction – Identifying patterns in stored data, based on the metadata extracted from the video stream. The better, and more elaborate this metadata is, the better the results and insights will be. The quality of the metadata relies on the quality of the analytics, and this is where advanced algorithms exhibited by deep learning
,come into play
https://hailo.ai/zh-hans/blog/ai-enhanced-video-management-scalability/
Solutions
AI Inference
Banking
Restaurant / POS
Medical
Security
Factory Automation
CANbus Application
Transportation
Kiosk and Self-service
Public Utilities
AI Inference
-
AICH1000 - AI Accelerator Kit powered by Hailo-8R
-
AI Surveillance Optimization - high efficiency, low consumption & flexible deployment
-
Scaling Up Video Management Systems(VMS)
-
Generative AI for Smart Cockpit / IVI
-
AI In Smart Retail
-
Hailo AI Processor for Personal Computers
-
Access Control & Identity Management
-
Intelligent Transportation Systems
-
Perimeter Protection
-
Hailo AI Processor for AOI
-
Hailo AI Processor for ADAS & AD
-
Optimize medical machines to improve accuracy and efficiency
-
PCB Manufacturing Intelligent AOI System
Scaling Up Video Management Systems(VMS)
Scaling Up Video Management Systems(VMS)

What is a video management system?
Video Management Systems, also known as VMS, collect inputs from multiple cameras and other sensors, addressing all related aspects of video handling, such as storage, retrieval, analysis and display. VMS are typically used in the security and surveillance space, enhancing personal safety in public areas, office buildings, transportation terminals, medical institutes, and more. Other typical uses include the extraction of business intelligence through user behavior analysis for the purpose of customer experience improvement in retail and other industries.
Traditionally, the analysis of multiple video streams used to be laborious, relying on human perception for visual identification of events happening across a multitude of video feeds. This method has many disadvantages as it is difficult to scale, violates people’s privacy, and is prone to errors due to operator’s fatigue, leading to false alarms, missed occurrences, and inefficient use of resources.
Nowadays, deep learning is enabling the automation of video analytics tasks, thereby allowing for scalability, and improvement in overall performance. This eventually leads to lower total cost of ownership (TCO).
According to a recent market research, the video management system market size is expected to reach $31B by 2027, growing at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 23.1% between 2022-2027. The key drivers for this growth are increasing security concerns and rapid adoption of IP cameras for surveillance, security, and retail applications.
AI-powered video analytics are being rapidly adopted for VMS
There are multiple possible configurations to a VMS system, depending on the number of video channels, the required video analytics applications, and the system cost. However, a typical video management system will include, in addition to cameras, an NVR or VMS server, a display (mobile phone, single or multiple screens, etc.) and storage space (local or cloud-based).

To enable real-time and accurate video analytics, Video Management Systems require high-performance computing. Artificial intelligence (AI) is transformational to this market as it allows faster and more accurate event identification at a lower cost. For this reason, AI-powered video analytics are being rapidly adopted by VMS software providers. AI video analytics could be introduced to any and all of the system components, e.g., at the data source on smart cameras, at the aggregation point such as smart gateways or network video recorders (NVRs), or in the cloud, which is sometimes administered as a service (VSaaS – video surveillance as a service). For a more detailed review of the different VMS configurations and how to design AI into each of them, refer to our whitepaper.
Introducing AI to the different system components provides multiple benefits:
- Enhanced safety – spotting relevant events, hazards, and regions of interest (ROIs) in each video stream, triggering response to pre-defined events, creating video metadata to enable history search, and enabling anonymization for improved privacy
- Improved network utilization – streaming relevant events only reduces bandwidth which results in further cost saving
- Improved storage utilization – removing irrelevant or uninteresting content to minimize storage space and enhance cost-efficiency
AI is fundamental for more accurate and safer VMS
The use of AI-powered video analytics in VMS is threefold: event detection, response triggering and data analysis.
Detect
The first layer of video analytics is scene understanding and metadata extraction for the purpose of both real-time response as well as long term storage for future search and analysis. Multiple neural networks can be deployed for this phase, leveraging advanced algorithms to perform deep-learning tasks. These tasks serve as the foundation on which more complex tasks identify pre-defined events and trigger specific response.
- Object Recognition – identify specific objects or a class of objects within a frame, and could be used to distinguish between classes of objects
- Counting – count the number of objects in a specific area, especially in places where occupancy is limited and has safety implications
- Density estimation – identify an evolving situation. Unlike counting, this is relevant in cases in which the exact number of objects is not required, but rather their overall density
- Object attributes – assist in unique identification of a person or an object in a specific scene, or re-identification of the same unique entity in the same scene over time, or across multiple scenes
- Gesture estimation – analyze a sequence of gestures which enables interpretation of specific behaviors for the purpose of behavioral analysis
- Distance measurement – calculate the distance between two or more people or objects, based on the accurate 3D location of each entity in a defined space
Respond
The second layer of video analytics is real-time event triggering based on insights from the detection phase. In this phase, pre-defined events trigger specific responses, such as setting off an alarm or alerting operators, security personnel or first responders, or triggering end-point actuators, for example to grant access for authorized personnel.
A few common applications used for AI-based response are:
- Crowd Management – through people and vehicle counting, and density estimation, the accumulation of large number of entities creates an event in a specific location which may trigger a response or call to action such as load balancing and dynamic traffic management
- Perimeter Protection – face and person attributes as well as gesture estimation and distance measurement, can all serve to secure and protect an area with restricted access or an unsafe zone
- Social Distancing – detecting whether people maintain social distancing in public places, supporting health authorities in their effort to contain a pandemic
- Behavioral Analysis – recognizing distress signals and triggering an alert to call first responders to the scene as soon as possible, and much faster than a call to 911 would
- Lost Person / Unattended Object – helpful for security personnel searching for lost people/luggage, or tracking down suspects, based on property indexing and gesture estimation
- License Plate Recognition (LPR) – used for access control and billing in parking lots or garages
Analyze
The third layer in video analytics is indexing, storage and retrieval of metadata.
Artificial intelligence is leveraged to cost-efficiently index and store relevant information from video streams. Deep, actionable insights can be extracted by exploring patterns over long-term observations and joint analysis of multiple points of view. This can be employed for the following purposes:
- Indexing & Recording – efficiently manage the data and reduce communication and storage costs, artificial intelligence is used to differentiate between meaningful events and background footage. This enables the system to record and store only significant events as defined by the user
- Summarization – used to create an edited and concise digest of the camera input, which only includes the significant events and insights, cropping out irrelevant footage
-
Data Extraction – Identifying patterns in stored data, based on the metadata extracted from the video stream. The better, and more elaborate this metadata is, the better the results and insights will be. The quality of the metadata relies on the quality of the analytics, and this is where advanced algorithms exhibited by deep learning
,come into play
https://hailo.ai/zh-hans/blog/ai-enhanced-video-management-scalability/
Solutions
AI Inference
Banking
Restaurant / POS
Medical
Security
Factory Automation
CANbus Application
Transportation
Kiosk and Self-service
Public Utilities
AI Inference
-
AICH1000 - AI Accelerator Kit powered by Hailo-8R
-
AI Surveillance Optimization - high efficiency, low consumption & flexible deployment
-
Scaling Up Video Management Systems(VMS)
-
Generative AI for Smart Cockpit / IVI
-
AI In Smart Retail
-
Hailo AI Processor for Personal Computers
-
Access Control & Identity Management
-
Intelligent Transportation Systems
-
Perimeter Protection
-
Hailo AI Processor for AOI
-
Hailo AI Processor for ADAS & AD
-
Optimize medical machines to improve accuracy and efficiency
-
PCB Manufacturing Intelligent AOI System
Scaling Up Video Management Systems(VMS)
Scaling Up Video Management Systems(VMS)

What is a video management system?
Video Management Systems, also known as VMS, collect inputs from multiple cameras and other sensors, addressing all related aspects of video handling, such as storage, retrieval, analysis and display. VMS are typically used in the security and surveillance space, enhancing personal safety in public areas, office buildings, transportation terminals, medical institutes, and more. Other typical uses include the extraction of business intelligence through user behavior analysis for the purpose of customer experience improvement in retail and other industries.
Traditionally, the analysis of multiple video streams used to be laborious, relying on human perception for visual identification of events happening across a multitude of video feeds. This method has many disadvantages as it is difficult to scale, violates people’s privacy, and is prone to errors due to operator’s fatigue, leading to false alarms, missed occurrences, and inefficient use of resources.
Nowadays, deep learning is enabling the automation of video analytics tasks, thereby allowing for scalability, and improvement in overall performance. This eventually leads to lower total cost of ownership (TCO).
According to a recent market research, the video management system market size is expected to reach $31B by 2027, growing at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 23.1% between 2022-2027. The key drivers for this growth are increasing security concerns and rapid adoption of IP cameras for surveillance, security, and retail applications.
AI-powered video analytics are being rapidly adopted for VMS
There are multiple possible configurations to a VMS system, depending on the number of video channels, the required video analytics applications, and the system cost. However, a typical video management system will include, in addition to cameras, an NVR or VMS server, a display (mobile phone, single or multiple screens, etc.) and storage space (local or cloud-based).

To enable real-time and accurate video analytics, Video Management Systems require high-performance computing. Artificial intelligence (AI) is transformational to this market as it allows faster and more accurate event identification at a lower cost. For this reason, AI-powered video analytics are being rapidly adopted by VMS software providers. AI video analytics could be introduced to any and all of the system components, e.g., at the data source on smart cameras, at the aggregation point such as smart gateways or network video recorders (NVRs), or in the cloud, which is sometimes administered as a service (VSaaS – video surveillance as a service). For a more detailed review of the different VMS configurations and how to design AI into each of them, refer to our whitepaper.
Introducing AI to the different system components provides multiple benefits:
- Enhanced safety – spotting relevant events, hazards, and regions of interest (ROIs) in each video stream, triggering response to pre-defined events, creating video metadata to enable history search, and enabling anonymization for improved privacy
- Improved network utilization – streaming relevant events only reduces bandwidth which results in further cost saving
- Improved storage utilization – removing irrelevant or uninteresting content to minimize storage space and enhance cost-efficiency
AI is fundamental for more accurate and safer VMS
The use of AI-powered video analytics in VMS is threefold: event detection, response triggering and data analysis.
Detect
The first layer of video analytics is scene understanding and metadata extraction for the purpose of both real-time response as well as long term storage for future search and analysis. Multiple neural networks can be deployed for this phase, leveraging advanced algorithms to perform deep-learning tasks. These tasks serve as the foundation on which more complex tasks identify pre-defined events and trigger specific response.
- Object Recognition – identify specific objects or a class of objects within a frame, and could be used to distinguish between classes of objects
- Counting – count the number of objects in a specific area, especially in places where occupancy is limited and has safety implications
- Density estimation – identify an evolving situation. Unlike counting, this is relevant in cases in which the exact number of objects is not required, but rather their overall density
- Object attributes – assist in unique identification of a person or an object in a specific scene, or re-identification of the same unique entity in the same scene over time, or across multiple scenes
- Gesture estimation – analyze a sequence of gestures which enables interpretation of specific behaviors for the purpose of behavioral analysis
- Distance measurement – calculate the distance between two or more people or objects, based on the accurate 3D location of each entity in a defined space
Respond
The second layer of video analytics is real-time event triggering based on insights from the detection phase. In this phase, pre-defined events trigger specific responses, such as setting off an alarm or alerting operators, security personnel or first responders, or triggering end-point actuators, for example to grant access for authorized personnel.
A few common applications used for AI-based response are:
- Crowd Management – through people and vehicle counting, and density estimation, the accumulation of large number of entities creates an event in a specific location which may trigger a response or call to action such as load balancing and dynamic traffic management
- Perimeter Protection – face and person attributes as well as gesture estimation and distance measurement, can all serve to secure and protect an area with restricted access or an unsafe zone
- Social Distancing – detecting whether people maintain social distancing in public places, supporting health authorities in their effort to contain a pandemic
- Behavioral Analysis – recognizing distress signals and triggering an alert to call first responders to the scene as soon as possible, and much faster than a call to 911 would
- Lost Person / Unattended Object – helpful for security personnel searching for lost people/luggage, or tracking down suspects, based on property indexing and gesture estimation
- License Plate Recognition (LPR) – used for access control and billing in parking lots or garages
Analyze
The third layer in video analytics is indexing, storage and retrieval of metadata.
Artificial intelligence is leveraged to cost-efficiently index and store relevant information from video streams. Deep, actionable insights can be extracted by exploring patterns over long-term observations and joint analysis of multiple points of view. This can be employed for the following purposes:
- Indexing & Recording – efficiently manage the data and reduce communication and storage costs, artificial intelligence is used to differentiate between meaningful events and background footage. This enables the system to record and store only significant events as defined by the user
- Summarization – used to create an edited and concise digest of the camera input, which only includes the significant events and insights, cropping out irrelevant footage
-
Data Extraction – Identifying patterns in stored data, based on the metadata extracted from the video stream. The better, and more elaborate this metadata is, the better the results and insights will be. The quality of the metadata relies on the quality of the analytics, and this is where advanced algorithms exhibited by deep learning
,come into play
https://hailo.ai/zh-hans/blog/ai-enhanced-video-management-scalability/
Solutions
AI Inference
Banking
Restaurant / POS
Medical
Security
Factory Automation
CANbus Application
Transportation
Kiosk and Self-service
Public Utilities
AI Inference
-
AICH1000 - AI Accelerator Kit powered by Hailo-8R
-
AI Surveillance Optimization - high efficiency, low consumption & flexible deployment
-
Scaling Up Video Management Systems(VMS)
-
Generative AI for Smart Cockpit / IVI
-
AI In Smart Retail
-
Hailo AI Processor for Personal Computers
-
Access Control & Identity Management
-
Intelligent Transportation Systems
-
Perimeter Protection
-
Hailo AI Processor for AOI
-
Hailo AI Processor for ADAS & AD
-
Optimize medical machines to improve accuracy and efficiency
-
PCB Manufacturing Intelligent AOI System









